MAINTENANCE
It may come to a point when you need to decide if it’s financially practical to keep up your old HVAC system. If it’s costing you more to maintain your system than it is to run it you may want to consider a new system.

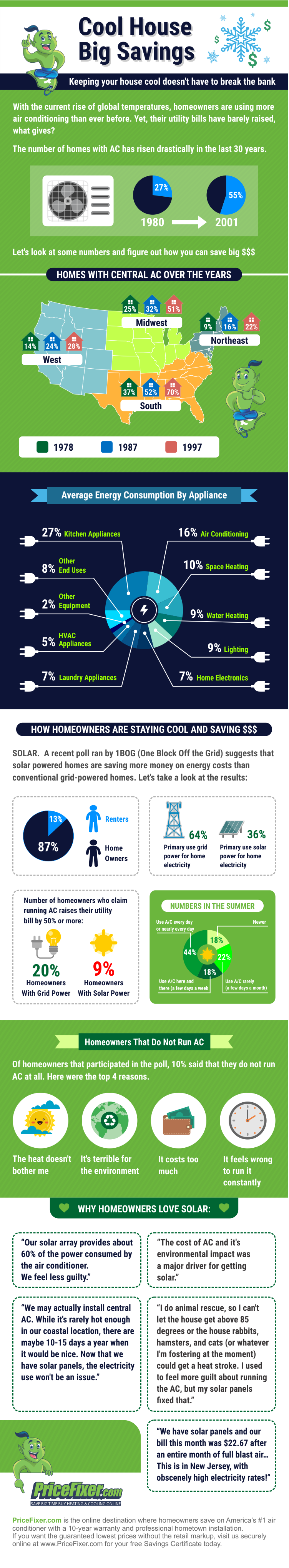
It is recommended that your HVAC system be serviced TWICE a year.
Over a 10-year period the cost of a new HVAC system could be 50% less than maintaining and repairing old equipment.

Air filters should be changed every 60-90 days. Clean filters lower electricity use by 5-15%.
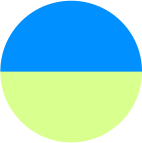
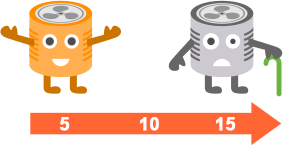
If your ratio is off, it may be time to upgrade. The recommended ratio for HVAC maintenance is:
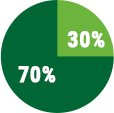
Preventative
Maintenance
Corrective
Maintenance